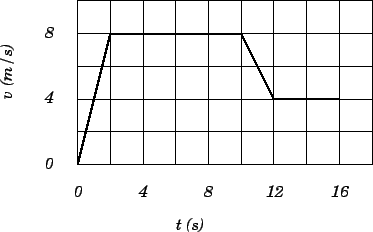
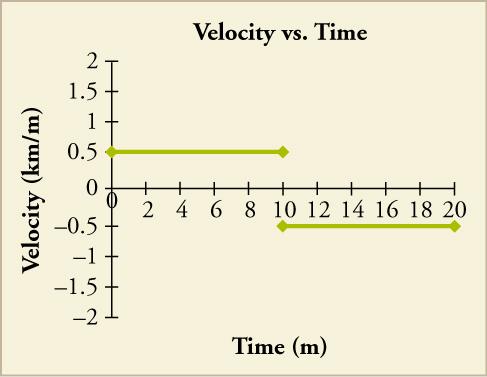
40 graphing velocity vs time worksheet
successessays.comSuccess Essays - Assisting students with assignments online You can contact us any time of day and night with any questions; we'll always be happy to help you out. Free Features. $15.99 Plagiarism report. $7.99 Formatting. › class › circlesNewton's Law of Universal Gravitation - Physics Classroom The solution of the problem involves substituting known values of G (6.673 x 10-11 N m 2 /kg 2), m 1 (5.98 x 10 24 kg), m 2 (70 kg) and d (6.39 x 10 6 m) into the universal gravitation equation and solving for F grav.
openstax.org › pages › 2-2-speed-and-velocity2.2 Speed and Velocity - Physics | OpenStax Instantaneous velocity and average velocity are the same if the velocity is constant. Figure 2.9 The diagram shows a more detailed record of an airplane passenger heading toward the back of the plane, showing smaller segments of his trip.

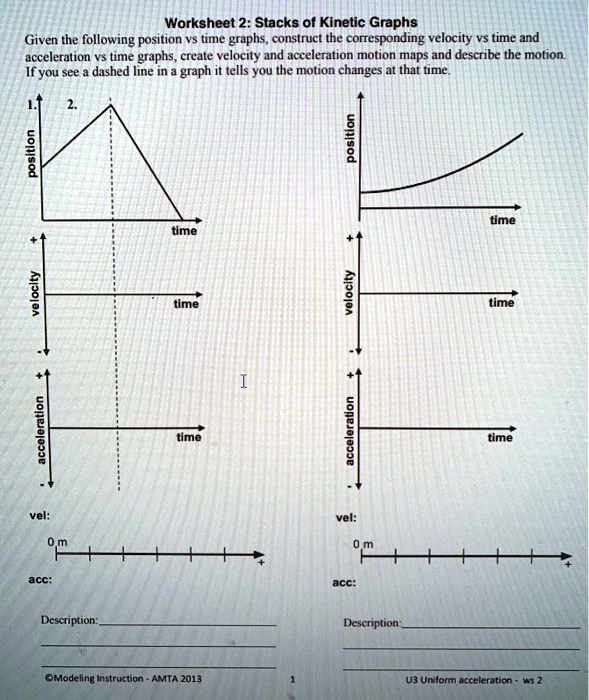
Graphing velocity vs time worksheet
› Speed-and-VelocitySpeed versus Velocity - Physics Classroom Speed, being a scalar quantity, is the rate at which an object covers distance. The average speed is the distance (a scalar quantity) per time ratio. Speed is ignorant of direction. On the other hand, velocity is a vector quantity; it is a direction-aware quantity. The average velocity is the displacement (a vector quantity) per time ratio. › class › newtlawsInertia and Mass - Physics Classroom Unbalanced forces cause objects to accelerate. But not all objects accelerate at the same rate when exposed to the same amount of unbalanced force. Inertia describes the relative amount of resistance to change that an object possesses. › class › energyPower - Physics Classroom Power is the rate at which work is done. It is the work/time ratio. Mathematically, it is computed using the following equation. Power = Work / time or P = W / t . The standard metric unit of power is the Watt. As is implied by the equation for power, a unit of power is equivalent to a unit of work divided by a unit of time.
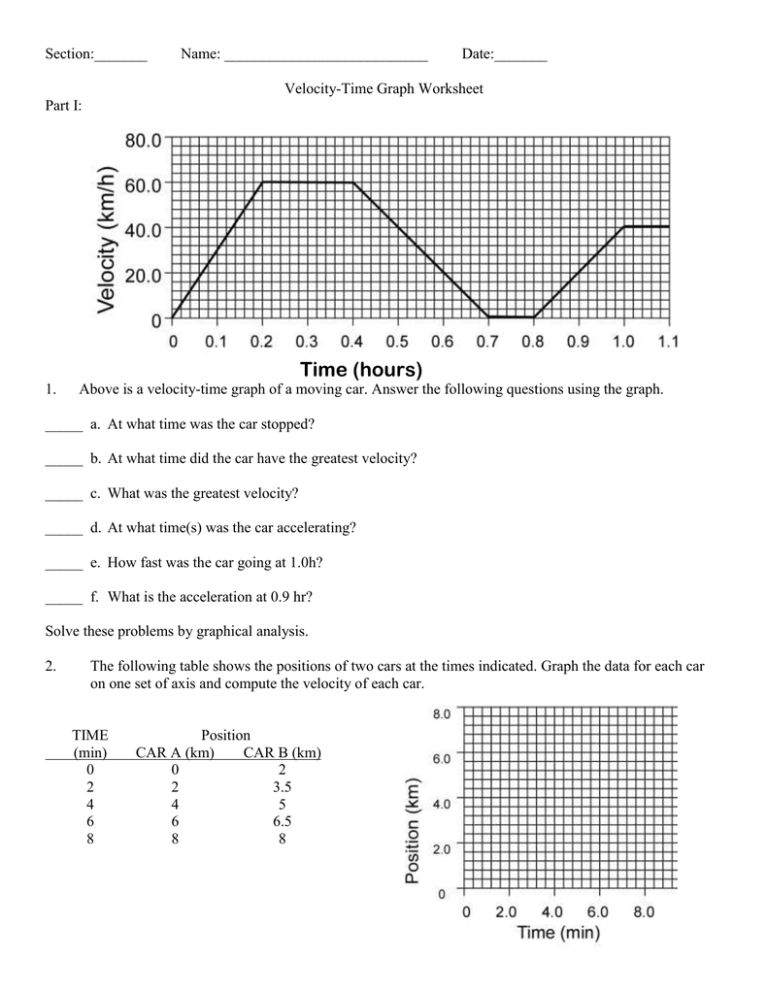
Graphing velocity vs time worksheet. › class › vectorsRelative Velocity and River Boat Problems - Physics Classroom a. It would require the same amount of time as before (20 s). Changing the current velocity does not affect the time required to cross the river since perpendicular components of motion are independent of each other. b. The distance traveled downstream is. d = v • t = (5 m/s) • (20.0 s) = 100 m. › class › energyPower - Physics Classroom Power is the rate at which work is done. It is the work/time ratio. Mathematically, it is computed using the following equation. Power = Work / time or P = W / t . The standard metric unit of power is the Watt. As is implied by the equation for power, a unit of power is equivalent to a unit of work divided by a unit of time. › class › newtlawsInertia and Mass - Physics Classroom Unbalanced forces cause objects to accelerate. But not all objects accelerate at the same rate when exposed to the same amount of unbalanced force. Inertia describes the relative amount of resistance to change that an object possesses. › Speed-and-VelocitySpeed versus Velocity - Physics Classroom Speed, being a scalar quantity, is the rate at which an object covers distance. The average speed is the distance (a scalar quantity) per time ratio. Speed is ignorant of direction. On the other hand, velocity is a vector quantity; it is a direction-aware quantity. The average velocity is the displacement (a vector quantity) per time ratio.


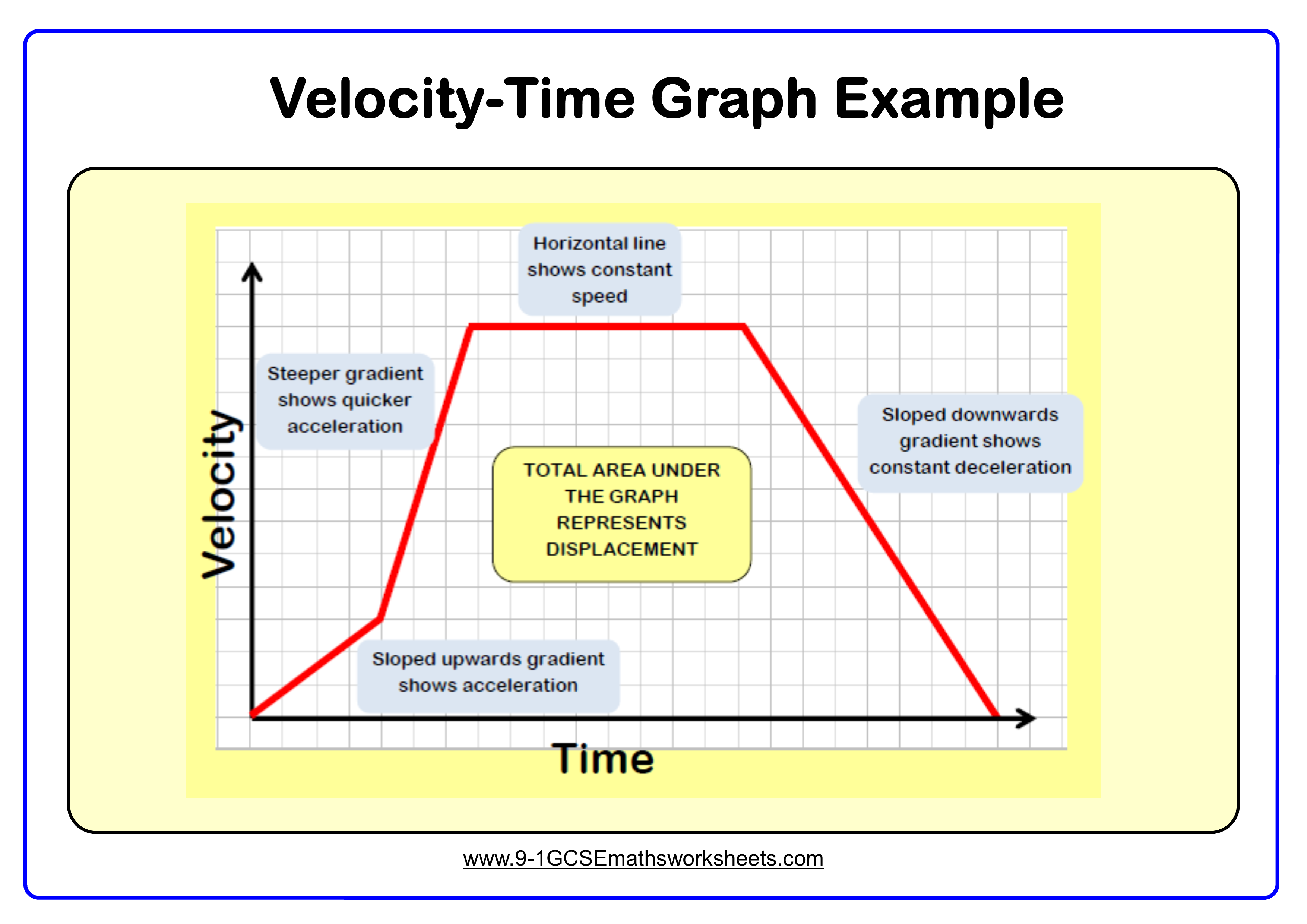

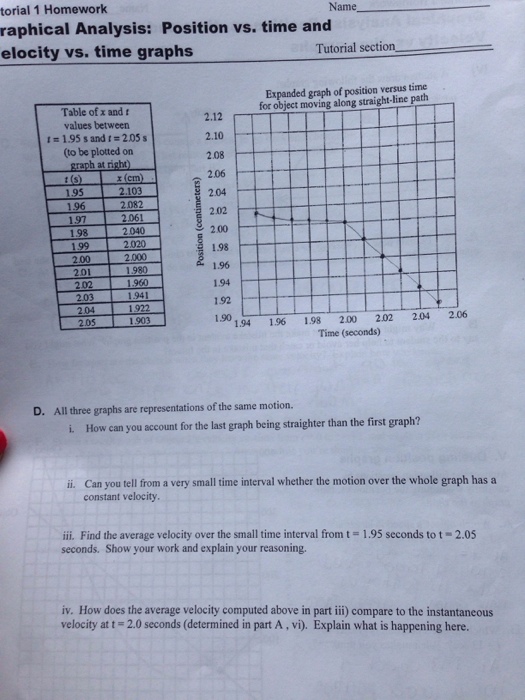

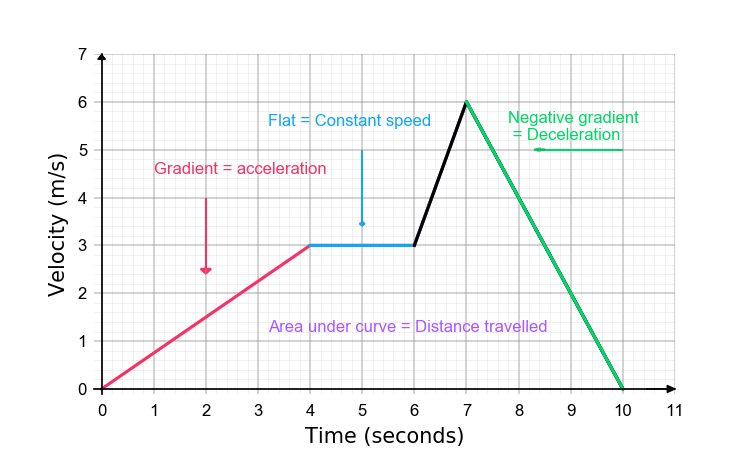

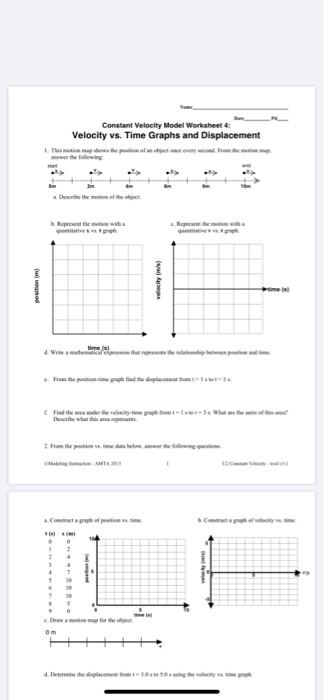




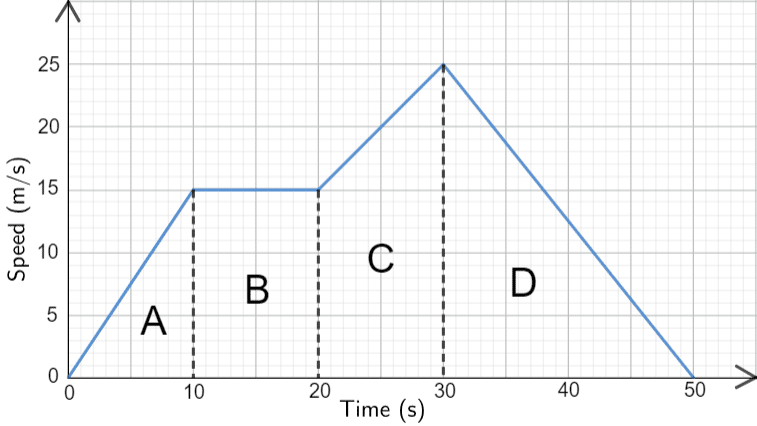








0 Response to "40 graphing velocity vs time worksheet"
Post a Comment