41 section 3.1 the rock cycle worksheet answers
3.1 The Rock Cycle - Physical Geology - 2nd Edition rock cycle, (Figure 3.1.1). The rock cycle is driven by two forces: (1) Earth's internal heat engine, which moves material around in the core and the mantle and leads to slow but significant changes within the crust, and (2) the hydrological cycle, which is the movement of water, ice, and air at the surface, and is powered by the sun. Rock Cycle Reading Teaching Resources | Teachers Pay Teachers The Owl Teacher by Tammy DeShaw. 4.9. (561) $7.50. PDF. Explore the earth science concepts of rocks and minerals with this engaging unit full of worksheets, investigation labs, reading passages, hands-on activities, and so much more as you explore the types of rocks, minerals, and the rock cycle!
Section 3.1 The Rock Cycle: Earth Science Flashcards | Quizlet Rock cycle, A model of the three basic rock types and the process of their formation, Magma, Molten material that forms deep beneath Earth's surface, Lava, Magma that reaches the surface, Igneous rock (formation) When magma is cooled and hardened, Sediments (formation) When rocks on the Earth's surface are broken down into smaller pieces,

Section 3.1 the rock cycle worksheet answers
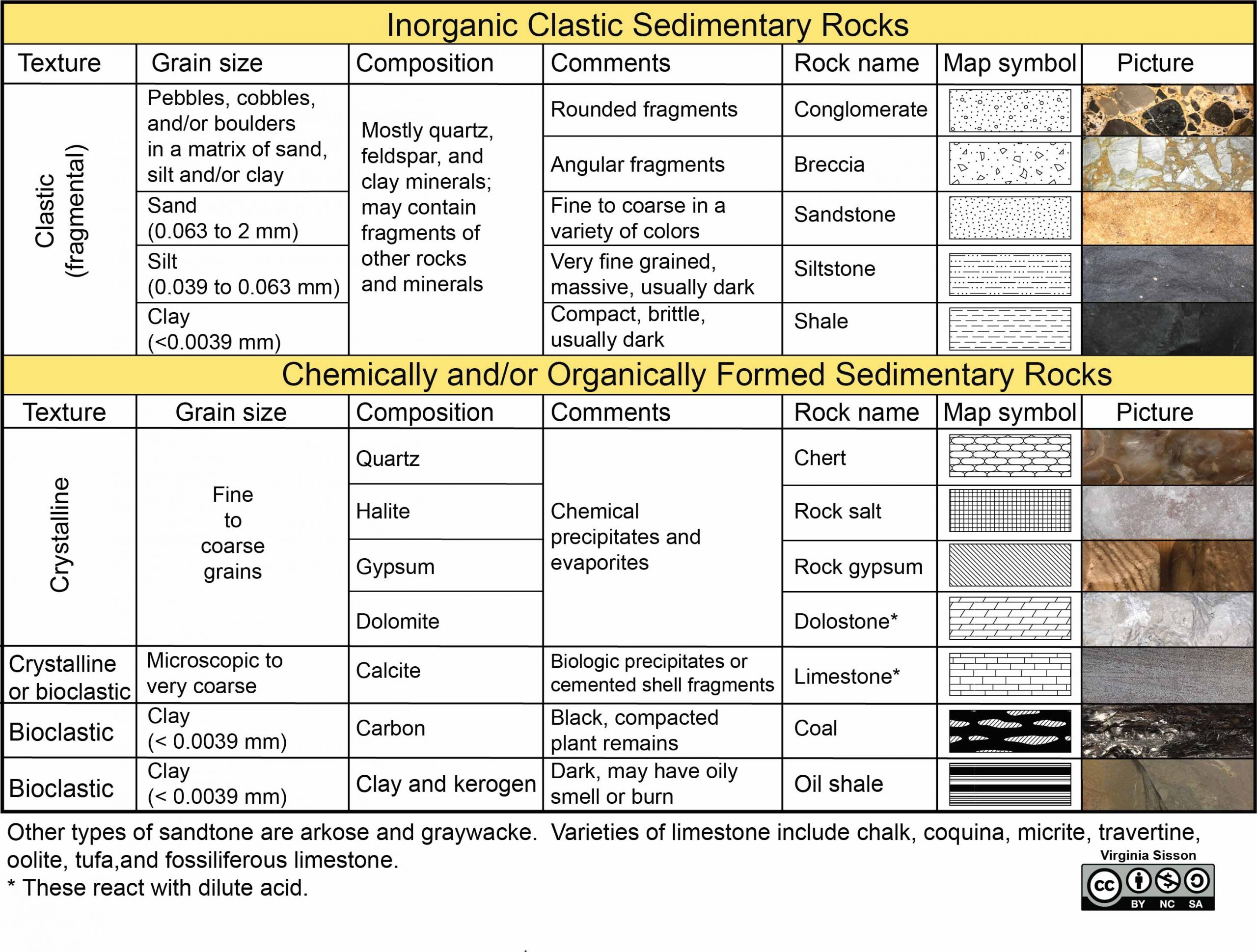
PDF Chapter 3 Rocks Section 3.1 The Rock Cycle - Weebly Chapter 3 Rocks Section 3.1 The Rock Cycle This section explains the different types of rocks found on Earth and in the rock cycle. Reading Strategy Building Vocabulary As you read, write down the definition for each term. For more information on this Reading Strategy, see the Reading and Study Skills in the Skills and Reference Handbook at the ... PDF Chapter 3 Rocks Section 3.1 The Rock Cycle - Ms. Murray's Biology 1. A(n) is any solid mass of mineral or mineral-like matter that occurs naturally as part of Earth. 2. Most rocks, such as granite, occur as a solid mixture of . 3. Is the following sentence true or false? A characteristic of rock is that each of the component minerals retains its properties in the mixture. 4. PDF Section 22.3 rocks and the rock cycle worksheet answers Section 22.3 rocks and the rock cycle worksheet answers, Continue, Section 22.3 rocks and the rock cycle worksheet answers, Figure 1. The different colors and textures seen in this rock are caused by the presence of different minerals. There are three types of rocks: fiery, sedimentary and metamorphic. Each of these guys is part of the rock cycle.
Section 3.1 the rock cycle worksheet answers. PDF Chapter 1 Introduction to Earth Science - Flagstaff Unified School District Chapter 3 Rocks Summary 3.1 The Rock Cycle A rock is any solid mass of mineral or mineral-like matter that occurs naturally as part of our planet. The three major types of rocks are igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks, and metamorphic rocks. Interactions among Earth's water, air, and land can cause rocks to change from one type to another. 1 Exercises on Metamorphic Rocks - University of Saskatchewan First Edition. Chapter 11 "Metamorphic Rocks" by Karen Tefend, CC BY-SA 4.0. View source. Last edited: 8 Jan 2020. Note: much of the overview material for this chapter is replicated in this exercise section for your reference as you complete the lab. You will NOT have access to your lab book or notes for the rock and mineral exam! Exercises on Sedimentary Rocks - Introductory Physical Geology ... First Edition. Chapter 10 "Sedimentary Rocks" by Bradley Deline, CC BY-SA 4.0. View source. Last edited: 8 Jan 2020. Note: much of the overview material for this chapter is replicated in this exercise section for your reference as you complete the lab. You will NOT have access to your lab book or notes for the rock and mineral exam! Solved ACTIVITY 4.3 Use Figure 4.7 on page 111 and the - Chegg Laboratory 4 Rock-Foming Processes and the Rock Cycle . 111 Rock-Forming Minerals Activity 4.3 Name: Course/Section: Date: A REFLECT & DISCUSS Refer to 9. 4.7 and identity each rockforming mineral below (M. M.3.1). Write its name below the picture.
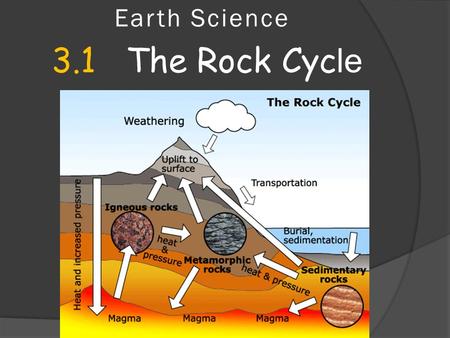
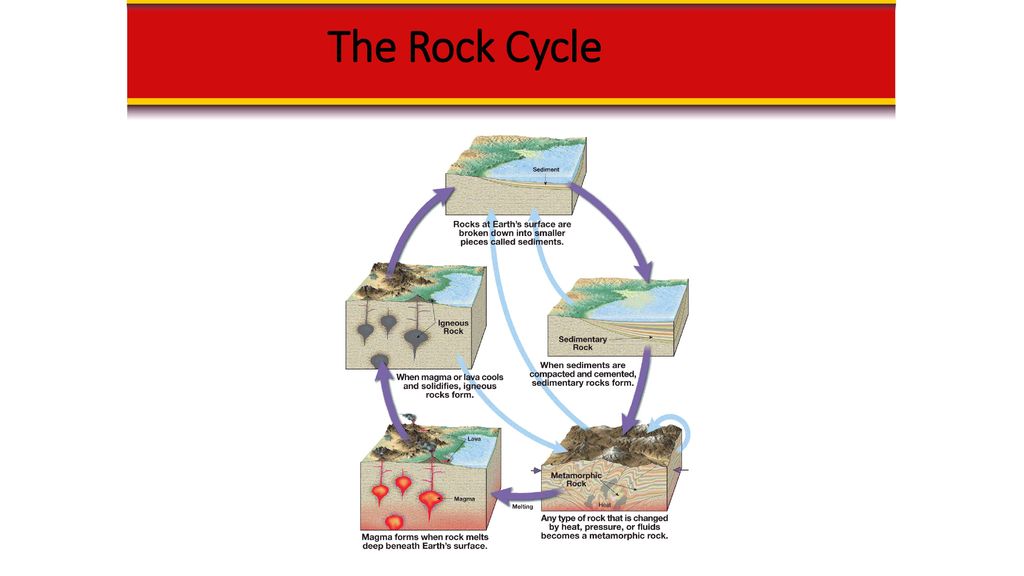
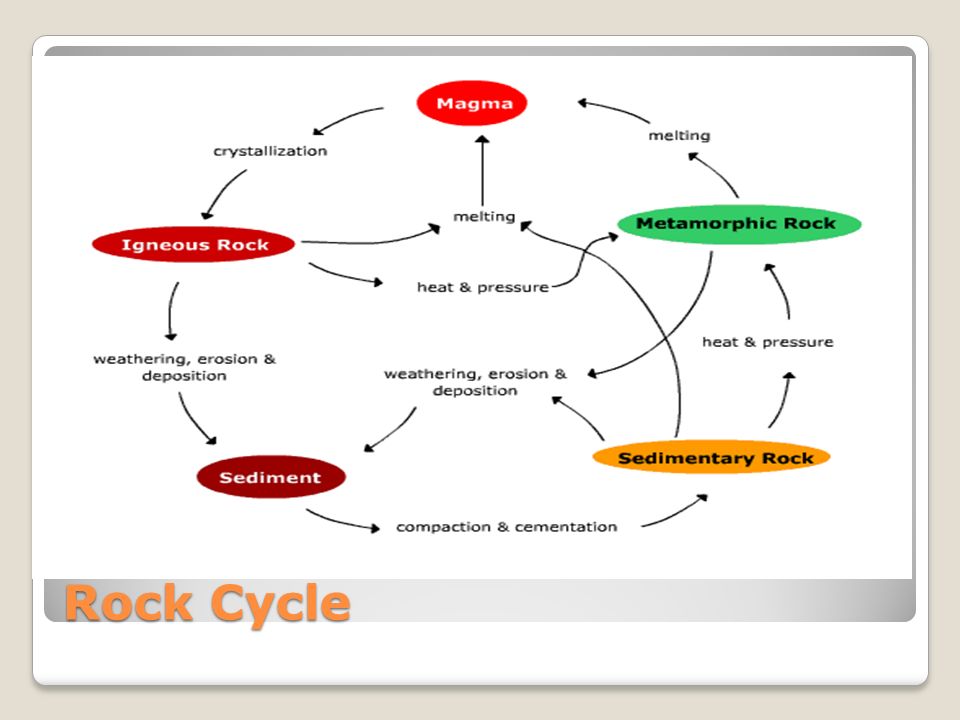
PDF Week: 12-14 Dates: 11/2-11/20 Unit: Rocks - Weebly Rocks, 1. A(n) is any solid mass of mineral or mineral-like matter that occurs naturally as part of Earth. 2. Most rocks, such as granite, occur as a solid mixture of . 3. Is the following sentence true or false? A characteristic of rock is that each of the component minerals retains its properties in the mixture. Rock Cycle Teaching Resources | Teachers Pay Teachers 4.8. (815) $5.50. PDF. Google Apps™. Activity. This rocks and minerals set of worksheets is a perfect supplemental resource to use for 2nd and 3rd grade. They cover types of rocks, what minerals and rocks are, properties of minerals, the rock cycle, geologists, and more. There are different types of resources, too. PDF Rocks and minerals and their exploitation Chapter 1 - Cambridge rock cycle (Figure 1.9). Table 1.1 compares the characteristics of the di erent rock types. Metamorphic rock: a rock formed from existing rocks by a combination of heat and pressure Rock cycle: a representation of the changes between the three rock types and the processes causing them KEY TERMS Igneous Sedimentary Metamorphic Made from liquid magma Chapter 3 pdf (1).pdf - Section 3.1 3.1 The Rock Cycle 1... - Course Hero The three major types of rocks are igneous rocks, sedi- mentary rocks, and metamorphic rocks. Before examining each group, you will look at a model for the rock cycle, which is the process that shows the relationships between the rock groups. What are the three types of rocks? The three types of Rocks are; Igneous Rocks, Sedimentary Rocks,
Chapter 6 The Rock Cycle | Physical Geology - GitHub Pages The processes involved are summarized in the rock cycle (Figure 6.3 ). The rock cycle is driven by two forces: Earth's internal heat, which causes material to move around in the core and mantle, driving plate tectonics. The hydrological cycle - movement of water, ice, and air at the surface. The hydrological cycle is powered by the sun. PDF Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE - SharpSchool 3.1 The Rock Cycle, Processes driven by heat from the Earth's interior are responsible for forming both igneous rock and metamorphic rock. External processes produce sedimentary rocks. Weathering and the movement of weathered materials are external processes powered by energy from the sun. Formation of Igneous Rocks, 3.2 Igneous Rocks, 1. 3.1 The Rock Cycle - Physical Geology - opentextbc.ca The rock cycle is driven by two forces: (1) Earth's internal heat engine, which moves material around in the core and the mantle and leads to slow but significant changes within the crust, and (2) the hydrological cycle, which is the movement of water, ice, and air at the surface, and is powered by the sun. Module 3.1 Quiz_ Rock Textures I.pdf - 6/10/2020 Quiz: Rock... They will be cohesiveCorrect AnswerCorrect Answer They will resemble clastic rocks 1.5 / 1.5 ptsQuestion 6 In a rock with a dual-sized crystalline texture, which would form first? They all form at the same time The small set of crystals The large set of crystalsCorrect!Correct!
8th Earth Science - Mr. Brever's Science Site 8th Grade Earth Science Course Curriculum Map Correlating to the State of Minnesota Science Standards
PDF Chapter 3 Rocks Section 3.1 The Rock Cycle - Flagstaff Unified School ... 1. A(n) is any solid mass of mineral or mineral-like matter that occurs naturally as part of Earth. 2. Most rocks, such as granite, occur as a solid mixture of . 3. Is the following sentence true or false? A characteristic of rock is that each of the component minerals retains its properties in the mixture.
Section 3.1 The Rock Cycle Flashcards | Quizlet rock cycle, a model that illustrates the origin of the three basic rock types and the interrelatedness of earth materials and processes, magma, a body of molten rock found at depth, including any dissolved gases and crystals, lava, magma that reaches earth's surface, weathering,
The Rock Cycle Worksheet Answer Key Pdf - myilibrary.org 3.1 The Rock Cycle - Physical Geology - BCcampus Open Publishing, The rock cycle is still active on Earth because our core is hot enough to keep the mantle moving, our atmosphere is relatively thick, and we have liquid water. , Lesson-plan-rock-cycle-experiment.docx - Casper College,
Acces PDF Answers To Rock Cycle - control.unap.edu.pe view Worksheet Answers. Middle School Rock Cycle Worksheet Answers. Middle School Rock Cycle Diagram Worksheet An-swers. CHAPTER 4 SECTION 1 The Rock Cycle Student Exploration: Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle. Get help with your The rock cycle homework. Access the answers to hundreds of The rock cycle questions that are explained in a way that's easy ...
PDF Directed Reading Packet Geosphere Unit - Central Bucks School District Section 3.1: The Rock Cycle This section explains the different types of rocks found on Earth and in the rock cycle. Reading Strategy Building Vocabulary As you read, write down the definition for each term. For more information on this Reading Strategy, see the Reading and Study Skills in the Skills and Reference Handbook at the end of
The Rock Cycle Review And Reinforce Answer Key Section 3.1 The Rock Cycle, matter that occurs naturally as part of Earth. 2. Most rocks occur as a solid mixture of . Circle the correct answer. minerals pumice. , Answer Key - StudyRes, TEACHER RESOURCES Answer Key Directed Reading A 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22.
Study documents, essay examples, research papers, course notes and ... Worksheet Section 13.1, Section 3.1 The Rock Cycle, Section 2.1 Matter, metamorphic rock - Mr. Meyer`s Science Page, Section 22.3 Rocks and the Rock Cycle, Informational Text: Rocks, Chapter 9, Rocks and the Rock Cycle, Water_Unit2, Relative Age Dating, bacteriogenic deposits, Chapter 6 The Rock and Fossil Record,
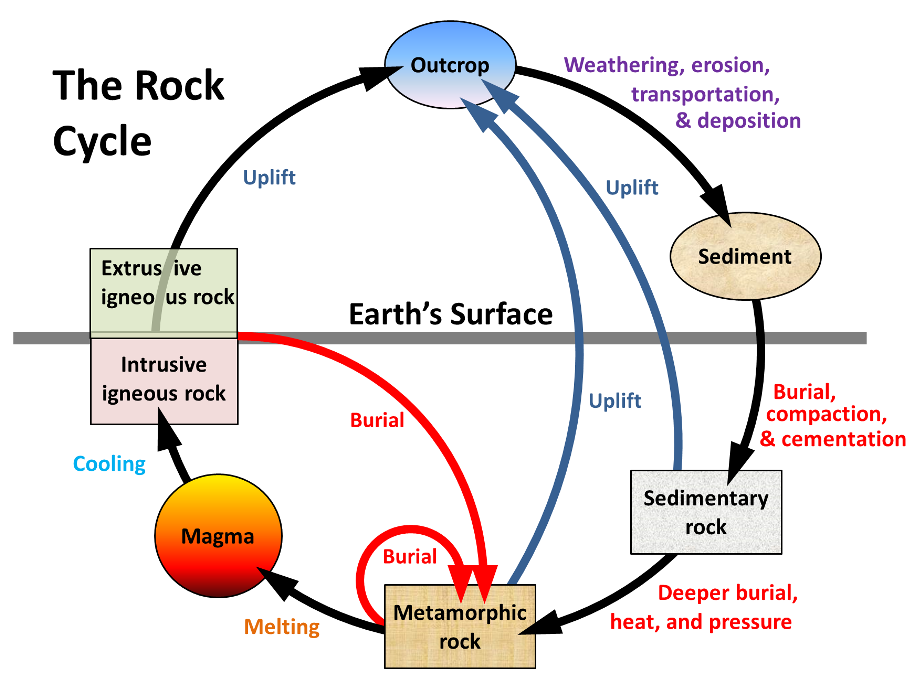
PDF Section 3.1 the rock cycle worksheet answer key - Weebly Section 3.1 the rock cycle worksheet answer key, A useful way to illustrate how the three main types of rock are related to one another and how changes to rocks happen in a recurring sequence is the rock cycle. It can be presented in a diagram like the one below.
PDF Section 3.1 the rock cycle worksheet answers - Weebly Section 3.1 the rock cycle worksheet answers, Is this what geologists mean by the rock cycle? Okay, very punny. The rock cycle shows how any type of rock can become any other type of rock.
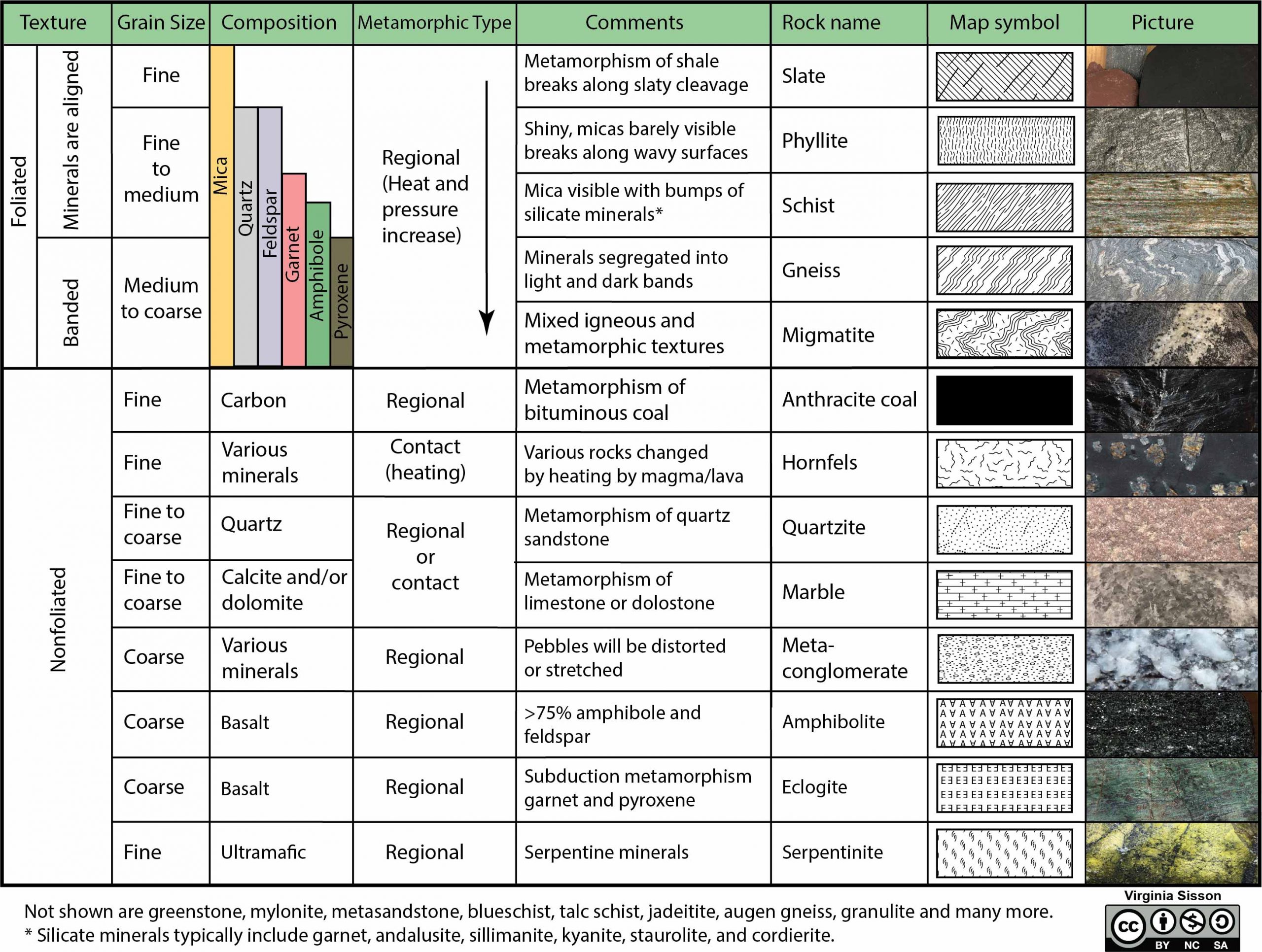
PDF Learning Assessment #2 Rock Cycle Answer Key Shale to Schist (Sedimentary to Metamorphic) 3.1Shale can become schist through neocrystallization (new crystallization of minerals from minerals that are not stable at higher temperatures and pressures) caused by an increase in temperature and/or pressure. This could occur as shale is incorporated into a collision zone and is regionally metamor...
PDF Section 22.3 rocks and the rock cycle worksheet answers Section 22.3 rocks and the rock cycle worksheet answers, Continue, Section 22.3 rocks and the rock cycle worksheet answers, Figure 1. The different colors and textures seen in this rock are caused by the presence of different minerals. There are three types of rocks: fiery, sedimentary and metamorphic. Each of these guys is part of the rock cycle.
PDF Chapter 3 Rocks Section 3.1 The Rock Cycle - Ms. Murray's Biology 1. A(n) is any solid mass of mineral or mineral-like matter that occurs naturally as part of Earth. 2. Most rocks, such as granite, occur as a solid mixture of . 3. Is the following sentence true or false? A characteristic of rock is that each of the component minerals retains its properties in the mixture. 4.
PDF Chapter 3 Rocks Section 3.1 The Rock Cycle - Weebly Chapter 3 Rocks Section 3.1 The Rock Cycle This section explains the different types of rocks found on Earth and in the rock cycle. Reading Strategy Building Vocabulary As you read, write down the definition for each term. For more information on this Reading Strategy, see the Reading and Study Skills in the Skills and Reference Handbook at the ...





















0 Response to "41 section 3.1 the rock cycle worksheet answers"
Post a Comment